What’s arthritis?
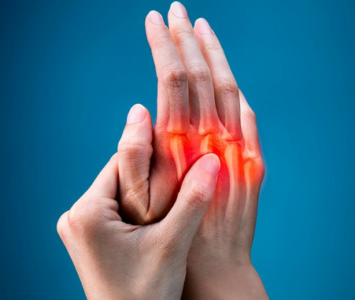
Arthritis is the inflammation of joints; wrist, fingers, hip, knee, ankle, etc.
Its pathophysiology involves tenderness, swelling, and stiffness that affects one or multiple joints. It’s also worth noting that if not managed pharmacologically, the symptoms of arthritis tend to worsen as time progresses.
Types of arthritis
There are many types of arthritis. The typing is based on a number of factors including age, cause, presentation, part of the body, etc. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Gout
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Septic arthritis
- Thumb arthritis
Also Read: Anti-Dandruff Hair Oils for Women and Men
In this post, we’ll major on the two most common types of arthritis:
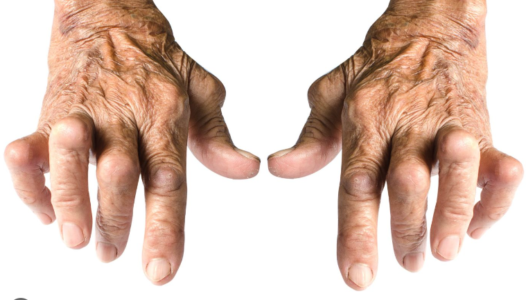
i.) Rheumatoid arthritis
This is an autoimmune disease that results when the body’s immune system attacks the joint capsule lining causing the synovial membrane to become inflamed and swollen. The inflammation along with impaired secretion of synovial fluid (joint lubricant) leads to pain, stiffness and sometimes immobility.
ii.) Osteoarthritis
A type of arthritis characterized by damage of the joint cartilage due to friction which causes wear and tear. In a normal joint, the cartilage protects the ends of bones from grinding on one another by acting as a cushion.
However, in Osteoarthritis, the cartilage gets damaged and thins out over time causing the bones to grind on each other, hence the pain associated with arthritis.
Quick Read: Tips on the Best Face Scrubs & Exfoliators for Teens
What causes arthritis?
The causes of arthritis vary depending on the particular type. Here are some common causes associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis:
1. Degeneration of the joint cartilage
This is seen in osteoarthritis where the degeneration of the joint cartilage causes increased friction leading to grinding of bones at the joint. In a normal joint, the cartilage acts as a cushion that absorbs stress and shock during joint movement.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the body’s immune system attacks the joint capsule lining thereby affecting the joint synovium, the tissue that secretes synovial fluid that lubricates the joint.
Because of the impaired secretion of the joint lubricant and tissue inflammation, the joints become stiff and painful during movement. The reasons behind the immune system’s attack on the synovium aren’t very unclear.
Quick Read: Best Beauty Tips for Teenage Girls
Symptoms of arthritis
The signs and symptoms associated with arthritis may vary with the type. Even so, the following symptoms are common for all of them:
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Redness
What are the risk factors for arthritis?
There are a couple risk factors for arthritis. Here’s a round up of some of the most common ones:
1. Past joint injuries
Individuals who’ve had past joint injuries are more likely to develop arthritis compared to persons who’ve had no such injuries. This is especially true for deep injuries that interfere with the integrity of the synovium and the joint capsule.
2. Sex
Men are far more likely to develop gout than women. On the other hand, women are more at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis than men.
3. Advanced age
The risk of developing almost all types of arthritis increases with age. Whenever you experience severe joint pains for prolonged duration and you also have issue of joint pain, go for medical check up, especially if you have advanced in age.
4. Obesity
Obesity puts a lot of pressure and stress on the joints thus increasing the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
5. Family history
Arthritis has also been found to follow blood lines. Meaning, the offspring acquires the defective genes from the parents. For such unfortunate cases, one becomes a victim for the simple reason that he or she is a descendant of one or both parents who are arthritic.
Treatment for arthritis
There’s no cure for arthritis. However, the condition can be managed pharmacologically and non-pharmacologically. The management of Arthritis is aimed at reducing the pain and preserving the structure and functions of the joint. Here are some common medications used in the management of arthritis.
A). Pharmacological management
a). Analgesics
This is a broad class of drugs that relieve pain without inducing loss of consciousness. Here are other sub-classes of analgesics.
Examples:
- i). Drugs relieving pain but not inflammation e.g. paracetamol/ acetaminophen
These drugs relieve both pain and inflammation e.g.
- > Over the counter NSAIDs: Ibuprofen (Advil, etc.), Naproxen (Aleve), Apazone,phenylbutazone, piroxicam, tenoxicam, diclofenac.
- > Other NSAIDs are prescription only
b). Anti-inflammatory creams and ointments
This category of medications is applied topically on the skin. Their mechanism of action involves interfering with the pain transmission mechanism at the joint hence affords relief against arthritis.
Examples: Menthol and Capsaicin creams
c). Corticosteroids
This class of anti-arthritis medications not only reduces inflammation but also suppresses immunity.
Examples: methylprednisolone, cortisone, and prednisone
d). Biological Response Modifiers
The class constitutes drugs that target different immune proteins and cytokines involved in the process of inflammation.
Examples:
TNF-alpha blockers: adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept, abatacept, anakinra.
e). Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
This category of drugs is specially designed to decrease pain and inflammation at the joint thereby preserving the integrity, structure, and functions of joints.
Their mechanism of action involves stopping immune system cells and proteins from attacking the joints.
Examples: hydroxychloroquine, sulphasalazine, methotrexate, gold, cyclosporine, leflunomide, minocycline, azathioprine.
B). Alternative interventions
The above modes of treatment can be complemented with non-pharmacological therapies as well as surgery. They include:
i). Joint surgery
Your doctor may recommend surgery, if the medications and non-pharmacological measures aren’t helping much. There are a number of surgeries that can be undertaken in this regard. Some of them include:
ii). Joint fusion
The operation involves the removal of damaged ends of bones at the joint then fusing the ends together into a single unit. Such a joint might never function normally again. The procedure is often done on the wrist, ankle, and finger joints.
iii. Joint repair
The operation involve realigning and smoothing damaged ends of bones so as to minimize pain and improve the overall joint functionality.
iv. Joint replacement
As the name suggests, this procedure involves the removal and replacement of damaged joints with artificial ones. It’s normally done on the knee or hip joints.
Home Remedies & Lifestyle interventions
There are a whole lot of measures that can be used to manage arthritis symptoms without necessarily using medications. Here are some:
- Exercise:
Regular exercise is known to improve joint flexibility and health. For arthritis management, the following exercises are recommended:
>Bicycling
>Swimming
>Walking
>Use of elliptical machines
- Weight loss:
The more weight, the more pressure on the hip and knee joints. For obese patients, its imperative that you take concrete steps to lose some pounds. The interventions could be pharmacological or non-pharmacological. Choose whichever works for you.
Losing weight is not only good for your joints but also for your overall health.
- Use of heating pads or ice packs
These can also be used to provide temporary relief from joint pains due to arthritis. You can use them whenever the pain is too severe or while you wait for the medicines to take effect on the pain.
- Assistive devices
These are machines and gadgets that can be used to improve mobility and undertaking of your daily routine. Some of them include walkers, shoe inserts, canes, raised toilet seats, etc.
Quick Read: How to Maintain Mental health During the Pandemic
C). The use of alternative medicines
Even though there’s little evidence to support their efficacy for managing arthritis, many people continue to use alternative medicines to manage joint pains associated with the condition. Here are some typical examples of alternative remedies in current use.
- Chondroitin
Independent studies have shown that chondroitin does provide some degree of relief from arthritis joint pains. However, more research needs to be done in this respect.
- Glucosamine
There are claims among some users that glucosamine relieves mild to severe joint pains. There are no scientific research studies to prove this claim so far. Even so, you can give the users the benefit of doubt and give glucosamine a try.
- Joint massage
Massage is known to improve blood circulation and relieve muscle stiffness. Furthermore, massage has been found to reduce the release of cytokines and other molecules known to stimulate pain.
- Acupuncture
The remedy involves piercing specific locations of the skin with needles. The aim of acupuncture is to relieve many types of pains, including those caused by arthritis.
- Yoga
This type of exercise improves flexibility and movement at the joints. Moreover, yoga has also been found to improve blood circulation which is vital for healthy joints.
Quick Read: How to Prevent Hair Loss Due to Alopecia
Arthritis Diagnosis
The process of diagnosis process involves the following:
i. Physical examination
Involves checking of the join for signs of swelling, inflammation, redness, or warmth. Also, mobility and flexibility of the joints should also be checked.
ii. Lab tests
Involves drawing some fluid from the joint then analyzing it. Besides the joint fluid, urine and blood can also be analyzed for arthritis typing.
iii. Imaging techniques
- X-rays
Can be used to get a clear picture of the joint and assess the level of damage. This imaging technique can be used to check for bone spurs, loss of cartilage, and bone damage.
- CT scans
CT scans can visualize both bone and surrounding soft tissue. That’s a clear departure from X-Rays scanners that can only capture details of bony structures.
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound are used to image fluid containing structures, soft tissues, and cartilage. It makes use of high frequency sound waves.